9 National Inequality
9.1 National Inequality (MADM)
9.1.1 Rationale, Approach and implementation
Rationale: Scientific basis for the analysis
Sub-national analysis of health intervention coverage is essential for advancing universal health coverage (UHC), which aims to ensure equitable access to quality health services for all populations. National averages often mask critical disparities that exist across regions, districts, or population subgroups.
Monitoring sub-national data helps identify geographical areas where coverage is low, signaling potential inequities in health service access and prompting targeted interventions. This is particularly important for drawing attention to populations who are left behind and ensuring resources are directed where they are most needed.
Approach: Description of analytical steps
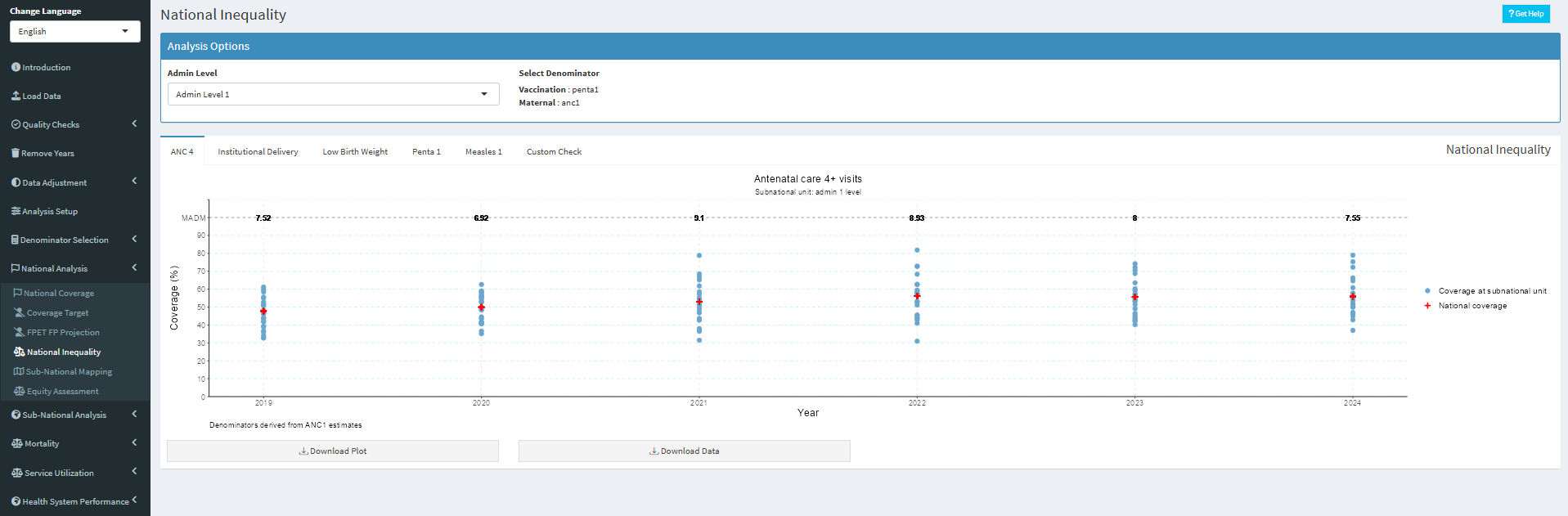
Here we calculate Median Absolute Deviation from the Median (MADM) to quantify spread in coverage in districts within an admin1 level , compared with the coverage at the said Admin1 subnational unit.
The key statistical measures for sub-national inequalities are:
MADM: median absolute distance from the median. This measure gives an indication on whether the country has been successful in reducing inequalities between sub-national units.
Percent of sub-national units with coverage above a specific target or threshold: this indicator provides information on the extent to which a country has been successful in reaching universal coverage at the sub-national level.
Summary of district and regional performance
Progress towards international and national targets can be measured by computing the percentage of regions and districts that have achieved these targets. The goal is for all regions and districts to have met the target. Higher percentages mean less inequality.
Implementation: Conducting analysis in the Shiny App
Navigate to the National Analysis =>National Inequality and inspect the plotted regional and district results by year, with the median absolute distance from the median (MADM, see screenshot below), as the summary measure to assess if inequalities have reduced.
Interpretation: